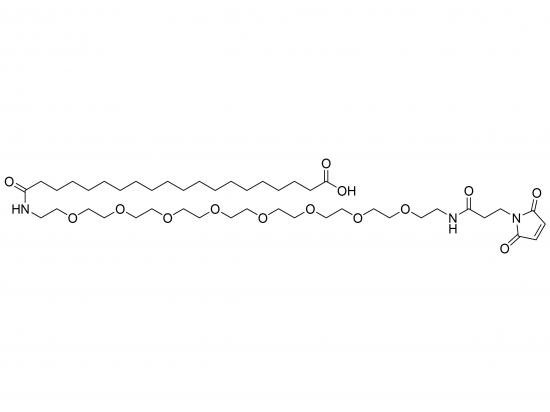
HO-Ara-NH-PEG9-NH-Mal is a synthetic heterobifunctional crosslinker designed for bioconjugation applications. It combines arabinose (Ara) with a free hydroxyl group, a nine-unit polyethylene glycol (PEG9) spacer providing hydrophilicity and flexibility, and a maleimide (Mal) group that reacts selectively with sulfhydryl (thiol) groups in cysteine residues. This linker enables stable thioether bond formation, facilitating conjugation of biomolecules like proteins, peptides, antibodies to carbohydrates, surfaces, or thiol-containing molecules. The defined PEG length ensures consistent performance and reduced nonspecific binding, making it valuable for targeted drug delivery and nanomaterial surface modification.
Appearance
-
White to off-white solid or viscous liquid
-
Often hygroscopic
Source
-
Chemically synthesized by specialized bioconjugation reagent manufacturers (e.g., Thermo Fisher Scientific, BroadPharm, Click Chemistry Tools)
-
Typically synthesized on demand, not widely stocked
Molecular Weight
-
Approximately 729.8 g/mol (theoretical value; may vary due to counterions, protecting groups, or residual solvents)
Structure
-
Arabinose (open-chain form) linked to one end of PEG9 chain via amide bond
-
PEG9 chain linked at other end to maleimide group via amide bond
Biological Activity
-
No intrinsic biological activity
-
Activity depends on molecules conjugated to linker
-
PEG spacer enhances biocompatibility and reduces immunogenicity
-
Arabinose may interact with lectins or carbohydrate-binding proteins
Purity and Microbial Contamination
| Purity and Microbial Contamination | Specification |
|---|---|
| Purity | >90%, ideally >95% by HPLC |
| Microbial contamination | Concern for in vivo use; minimize endotoxin levels |
| Certificate of Analysis (CoA) | Details purity, residual solvents, and endotoxin levels |
Identity and Quality Control
| Identity and Quality Control | Specification |
|---|---|
| Mass Spectrometry (MS) | Confirms molecular weight |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (¹H and ¹³C NMR) | Confirms chemical structure |
| High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) | Determines purity |
| Reactivity tests (e.g., with reducing agent, model thiol) | Verifies functionality of arabinose and maleimide groups |
Shelf Life and Storage
-
Store at -20°C under dry, inert atmosphere (argon or nitrogen)
-
Protect from light and moisture
-
Maleimide group sensitive to hydrolysis; avoid water exposure
-
Shelf life approximately 6–12 months with proper storage
Application
-
Protein-carbohydrate conjugation for targeted delivery or controlled release
-
Surface modification to attach biomolecules to carbohydrate-modified surfaces
-
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) via maleimide chemistry
-
Nanoparticle functionalization for targeted delivery
-
Crosslinking thiol-containing molecules with arabinose-reactive groups
Key Characteristics
-
Heterobifunctional: arabinose and maleimide reactive groups
-
Hydrophilic PEG9 spacer provides water solubility and reduces nonspecific binding
-
High biocompatibility due to PEG
-
Maleimide selectively reacts with thiols
-
Carbohydrate moiety (arabinose) allows sugar-mediated interactions
-
Defined PEG length ensures batch consistency
Citation
-
PEG Maleimide Chemistry: Search “PEGylation of proteins using maleimide chemistry”
-
Carbohydrate-Protein Conjugates: Search “Carbohydrate-modified proteins for targeted drug delivery”
-
Heterobifunctional PEG Linkers: Search “Heterobifunctional PEG linkers for protein crosslinking”
-
Maleimide-Thiol Coupling: Search “Maleimide-thiol coupling for controlled drug release”
-
Arabinose Targeting Ligand: Search “Arabinose-modified nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery”
-
PEGylation for Biocompatibility: Search “PEGylation for improved protein biocompatibility”
-
Click Chemistry in Bioconjugation: Search “Click chemistry for protein-carbohydrate bioconjugation”
-
Surface PEGylation: Search “PEGylation of surfaces to reduce protein adsorption”
-
ADCs Using Maleimide: Search “Maleimide-based antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy”
-
Reducing Sugar Conjugation: Search “Reductive amination in protein glycosylation”
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.