AEEA (2-[2-(2-aminoethoxy)ethoxy]acetic acid) is a short, hydrophilic, and biocompatible linker widely used in bioconjugation and peptide synthesis. It comprises an ethylene glycol chain terminated by an amine and a carboxylic acid group, allowing incorporation into various molecules through amide coupling. Its ethylene glycol backbone enhances water solubility, reduces aggregation, and improves bioavailability of conjugates. The flexibility of the chain minimizes steric hindrance, facilitating efficient binding of linked ligands to biological targets. AEEA is employed to attach targeting ligands, drugs, or imaging agents to biomolecules, surfaces, and nanoparticles. Due to its excellent biocompatibility, it is suitable for in vivo applications and helps minimize interference with biomolecule activity by spacing functional groups.
Appearance
-
Clear, colorless to slightly yellow liquid or white to off-white solid
-
Typically hygroscopic
Source
-
Chemically synthesized and commercially available from suppliers such as Sigma-Aldrich, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Iris Biotech
Molecular Weight
-
161.17 g/mol
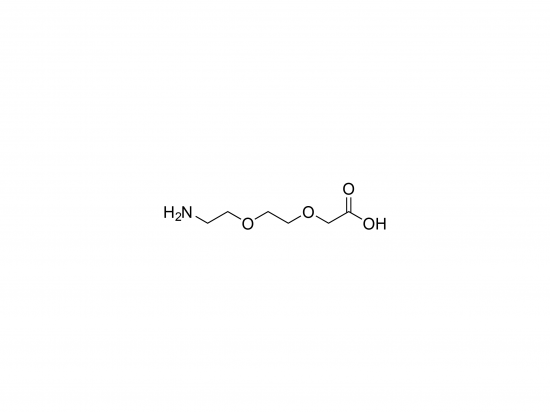
Structure
-
HOOC-CH₂-O-CH₂-CH₂-O-CH₂-CH₂-NH₂
Biological Activity
-
Generally biologically inert and biocompatible
-
Affects biological activity of conjugated molecules by enhancing solubility and bioavailability
Purity and Microbial Contamination
| Purity and Microbial Contamination | Specification |
|---|---|
| Purity | >95% by NMR or HPLC |
| Microbial contamination | Relevant for in vivo use |
| Endotoxin levels | Should be minimized |
| Certificate of Analysis (CoA) | Includes purity, residual solvents, endotoxin |
Identity and Quality Control
| Identity and Quality Control | Specification |
|---|---|
| Mass Spectrometry (MS) | Confirms identity |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (¹H and ¹³C NMR) | Confirms structure and purity |
| High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) or GC-MS | Assesses purity |
| Acidity | Verified by titration |
| Amine content | Determined by reaction with TNBS reagent |
Shelf Life and Storage
-
Store at −20°C under dry, inert atmosphere (argon or nitrogen)
-
Protect from light and moisture
-
Shelf life typically 1–2 years
Application
-
Peptide synthesis: as hydrophilic spacer incorporation
-
Bioconjugation: linking biomolecules, drugs, imaging agents
-
Polymer chemistry: monomer/building block for hydrophilic polymers
-
Surface modification: adding hydrophilic, functional groups
-
Drug delivery: improving solubility and bioavailability
Key Characteristics
-
Hydrophilic ethylene glycol backbone
-
Biocompatible and nontoxic
-
Flexible chain reduces steric hindrance
-
Bifunctional with terminal amine and carboxylic acid
-
Short spacer arm
Citation
-
“The Use of AEEA Linkers to Modulate the Solubility and Aggregation of Amyloid-β Peptides.” ACS Chemical Neuroscience, 2013.
-
“Solid-phase synthesis of constrained peptides using AEEA as a linker.” Tetrahedron Letters, 2006.
-
“Site-Specific PEGylation of Proteins Using AEEA Linkers.” Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2010.
-
“AEEA-based dendrimers for enhanced drug delivery.” Journal of Controlled Release, 2015.
-
“AEEA-modified surfaces for reduced protein adsorption.” Langmuir, 2012.
-
“AEEA-functionalized gold nanoparticles for sensitive biosensing.” Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2018.
-
“AEEA-containing hydrogels for cell encapsulation.” Biomacromolecules, 2014.
-
“Synthesis and properties of peptide nucleic acids containing AEEA linkers.” Nucleic Acids Research.
-
“AEEA spacer enhances conjugation efficiency of antibodies to nanoparticles.” Bioconjugate Chemistry.
-
“AEEA-modified imaging probes for improved tumor targeting.” Molecular Imaging.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.