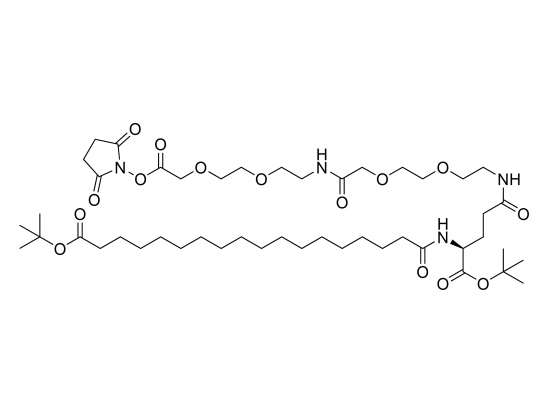
tBuO-Ste-Glu(AEEA-AEEA-OSu)-OtBu is a synthetic multifunctional building block designed for biomolecule modification, combining lipophilic and hydrophilic elements with a reactive conjugation site. It consists of a glutamic acid core where the alpha-amino group is linked to a stearic acid (Ste) moiety with a tert-butyl ester (tBuO) protecting group, one glutamic acid carboxyl is also tert-butyl protected (OtBu), and the other carboxyl group is connected through two AEEA (PEG-like) units ending in an N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS, OSu) ester for conjugation to primary amines.
Appearance
- White to off-white solid, potentially waxy due to the stearic acid chain.
Source
- Chemically synthesized; not naturally occurring.
- Available from specialized bioconjugation and lipid chemistry suppliers.
Molecular Weight and Structure
- Approximate molecular weight: 939.2 g/mol (C47H82N4O14).
- Structure includes stearic acid with tert-butyl protection, glutamic acid core, two PEG-like AEEA units forming a hydrophilic spacer, and terminal NHS ester.
Biological Activity
- Generally biologically inert alone; activity depends on conjugated molecules.
- Stearic acid provides membrane anchoring; AEEA spacer enhances solubility and reduces steric hindrance.
- NHS ester enables efficient conjugation to primary amines.
Purity and Microbial Contamination
- Typically ≥ 90% purity by HPLC.
- Microbial contamination minimal or absent; suppliers provide COAs.
- Tested with LAL assays and sterility tests.
Identity and Quality Control
- Confirmed by high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS), ¹H and ¹³C NMR spectroscopy, and IR spectroscopy.
- Purity determined by HPLC.
- NHS ester activity verified by amine quantification assays.
Shelf Life and Storage
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Shelf Life | Likely 6 months to 1 year; consult supplier COA for exact data |
| Storage | Store at -20°C or below in inert atmosphere, tightly sealed container; protect from moisture and light; NHS ester hydrolysis sensitive |
Applications
- Lipopeptide synthesis with hydrophilic spacers and reactive conjugation handles.
- Protein lipid modification for membrane targeting.
- Liposome formulation and surface modification.
- Bioconjugation reagent for linking molecules with lipid and PEG-like properties.
Key Characteristics
- Lipophilic stearic acid moiety enables membrane insertion.
- Hydrophilic PEG-like AEEA spacers improve solubility and reduce steric hindrance.
- Reactive NHS ester for primary amine conjugation.
- Acid-labile tert-butyl protecting groups allow controlled deprotection.
- Amphiphilic character combines hydrophilicity and lipophilicity.
Citation
-
Search “stearic acid protein modification” or “lipid protein conjugation.”
-
Search “PEGylation protein conjugation” or “AEEA spacer protein modification.”
-
Use “NHS ester protein conjugation” or “OSu ester conjugation.”
-
Look for “lipopeptide synthesis AEEA” and “PEGylated lipid modification.”
-
Supplier datasheets and application notes.
-
Chemical databases like Reaxys, SciFinder, PubChem.
-
Google Scholar with targeted terms “tBuO-Ste-Glu(AEEA-AEEA-OSu)-OtBu,” “lipopeptide synthesis,” “PEGylated lipid conjugation,” “stearyl protein modification.”
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.