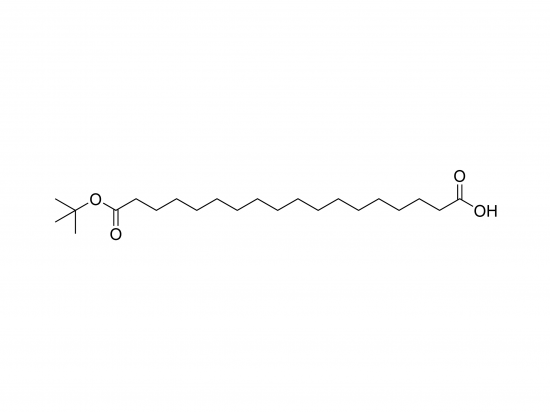
tBuO-Ste(OH) represents a chemically modified stearic acid molecule featuring a saturated 18-carbon fatty acid chain (stearic acid) with a carboxylic acid group (-COOH). The “tBuO-” denotes a tert-butoxy group attached to the stearic acid backbone, typically positioned at the omega carbon, introducing steric bulk and altering the molecule’s lipophilicity and steric environment. This tert-butyl ether modification is relatively stable under standard conditions but can be cleaved selectively under acidic environments, enabling controlled deprotection or release. The combination of the long hydrophobic alkyl chain and the hydrophilic carboxylic acid imparts amphiphilic character, allowing tBuO-Ste(OH) to serve as a versatile building block in synthesizing modified lipids, surfactants, and drug delivery systems. Depending on the precise position of the tert-butyl ether, the molecule’s physical properties and biological interactions can vary significantly. The modification may influence membrane fluidity, protein interactions, or drug delivery behavior while potentially acting as a fatty acid analog with limited metabolic degradation due to the bulky tBuO group.
Appearance
- Likely a white to off-white solid or waxy material, depending on purity and isomeric form.
Source
- Synthesized chemically via the introduction of the tert-butyl ether group onto a stearic acid derivative using targeted organic synthesis routes.
Molecular Weight and Structure
- Molecular weight estimated near 356.57 g/mol, assuming the tBuO group is attached at the terminal (omega) carbon. The structure can be described as (CH3)3C–O–(CH2)17–COOH with molecular formula C22H44O3.
Biological Activity
- Generally limited direct biological activity as a standalone molecule. Its biological relevance emerges when incorporated into larger constructs, where it may modulate membrane interactions, enhance drug-delivery characteristics, or resist enzymatic metabolism due to steric hindrance from the tert-butyl group.
Purity and Microbial Contamination
- High purity above 98% is preferred, especially for pharmaceutical or cosmetic uses. The compound should be free from microbial contamination, with suitable endotoxin levels, especially if used in biologically sensitive applications.
Identity and Quality Control
- Confirmed using analytical techniques including mass spectrometry (MS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and infrared spectroscopy (IR). Purity assessment may involve gas chromatography (GC), melting point determination, acid value, and Karl Fischer titration to evaluate moisture content.
Shelf Life and Storage
- Typically stable for 1–3 years when stored properly. Recommended storage is in tightly sealed containers, protected from moisture and light, at room temperature or under refrigeration.
Application
- Used in the synthesis of modified lipids and surfactants, as an intermediate in drug delivery system formulations, and as an additive in lubricants or polymer composites.
Key Characteristics
-
Retains the long hydrophobic stearic acid alkyl chain.
-
Tert-butyl ether group modifies lipophilicity and steric profile.
-
Exhibits amphiphilic properties depending on the tBuO group’s position.
-
Solid or waxy at room temperature, useful in material and formulation sciences.
Citation
-
The Lipid Handbook by Gunstone et al., CRC Press, 2007,
-
Lipid Analysis by Christie & Han, Oily Press, 2010,
-
Greene’s Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis by Wuts & Greene, Wiley, 2006,
-
Reviews on fatty acid derivative syntheses in Progress in Lipid Research,
-
Lipid classification and synthesis in the Journal of Lipid Research,
-
And supplier catalogs such as Sigma-Aldrich for chemical and safety data.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.