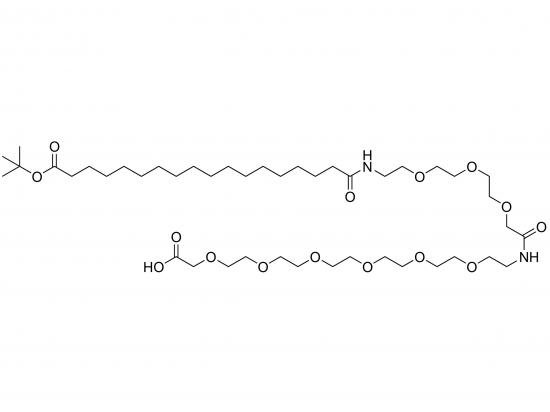
tBuO-Ste-AEEA-AEEA-OH is a synthetic compound designed to modify surfaces, lipids, or biomolecules by providing both a lipophilic anchor and a hydrophilic, PEG-like spacer with a reactive terminal carboxyl group. It features a stearic acid (Ste) moiety whose carboxyl is protected as a tert-butyl ester (tBuO), linked to two sequential AEEA (2-[2-(2-aminoethoxy)ethoxy]acetic acid) units, terminating in a free carboxyl group (OH). This structure enables incorporation of both hydrophobic and hydrophilic characteristics, selective conjugation via the free acid, and controlled deprotection during chemical synthesis or bioconjugation.
Appearance
-
White to off-white solid, potentially waxy due to the stearic acid chain
Source
-
Synthetically produced by chemical synthesis
-
Typically available from specialized suppliers in PEGylation, lipid modification, and bioconjugation reagents
Molecular Weight
-
Estimated between 650–900 g/mol, calculated precisely from constituent fragments
Structure
-
Stearic acid (tBuO-protected) linked to two sequential AEEA units via amide bonds
-
Terminal carboxyl group (OH) for further conjugation
Biological Activity
-
Generally biologically inert alone
-
Stearic acid enables membrane insertion/hydrophobic interactions
-
AEEA spacer confers water solubility, biocompatibility, and flexibility
-
Terminal acid can be activated for conjugation to additional molecules
Purity and Microbial Contamination
| Purity and Microbial Contamination | Specification |
|---|---|
| Purity | Typically ≥90%, verified by HPLC |
| Microbial contamination | Should be minimal, especially in vivo |
| Testing | LAL assay for endotoxin, sterility tests |
| Certificate of Analysis (CoA) | Details on purity, residuals, endotoxin |
Identity and Quality Control
| Identity and Quality Control | Specification |
|---|---|
| Mass Spectrometry (MS) | Confirms molecular weight |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (¹H, ¹³C NMR) | Confirms structure, purity |
| Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy | Verifies functional group presence |
| High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) | Determines purity |
| Acid value determination | Quantifies free carboxyl group |
Shelf Life and Storage
-
Shelf life likely shorter due to complexity; estimate 6–12 months
-
Store at –20°C or below, under inert atmosphere (argon or nitrogen), airtight and dry
-
Protect from light and moisture
Applications
-
Liposome formation: component for surface functionality and stability
-
Micelle formation: hydrophobic/hydrophilic structural element
-
Surface modification: coating surfaces with amphiphilic properties
-
Drug delivery: creating carriers with improved solubility and targeted membrane insertion
-
Bioconjugation: attaching molecules to lipids or hydrophobic surfaces via reactive carboxyl group
Key Characteristics
-
Lipophilic stearic acid chain for membrane affinity
-
Hydrophilic AEEA units for PEG-like solubility
-
Reactive terminal carboxyl for conjugation
-
tBu protection enables selective deprotection during synthesis
Citation
-
Search “stearic acid liposome” or “micelle formation with stearic acid”
-
Search “PEGylated lipid” or “AEEA modification in lipids”
-
Explore “carboxyl group activation lipid” for bioconjugation methods
-
Check specialized supplier technical sheets for related reagents
-
Use Reaxys, SciFinder for chemical fragment literature
-
Keywords for Google Scholar: “amphiphilic lipid polymer,” “AEEA lipid modification,” “PEGylation for liposome stability,” “stearic acid membrane insertion”
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.