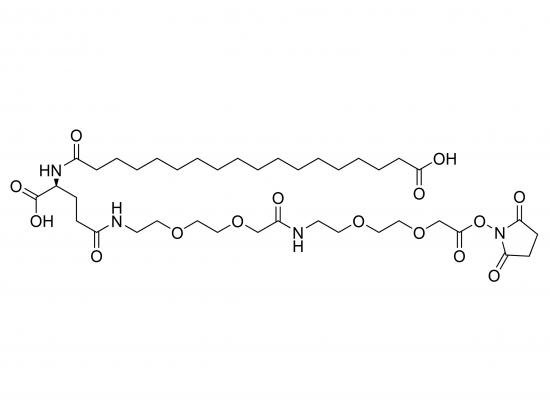
HO-Ste-Glu(AEEA-AEEA-OSu)-OH is a synthetic heterobifunctional crosslinker based on a glutamic acid (Glu) scaffold. It contains a lipophilic stearic acid (Ste) moiety at the α-carboxyl position, linked via an ester or amide bond, and an N-hydroxysuccinimide (OSu) ester attached to the γ-carboxyl through two hydrophilic and flexible AEEA (2-[2-(2-aminoethoxy)ethoxy]acetic acid) units. The stearic acid offers membrane anchoring or hydrophobic interactions, while the OSu ester reacts specifically with primary amines to form stable amide bonds, facilitating conjugation to amine-containing molecules. The glutamic acid backbone allows further modification, supporting the development of membrane-targeting drug delivery systems, protein surface modifications, and novel amphiphilic biomaterials.
Appearance
-
White to off-white solid or viscous liquid
-
Amphiphilic, potentially forming micelles in aqueous solutions
Source
-
Chemically synthesized by specialized bioconjugation reagent manufacturers or custom synthesis labs
-
Usually not a generally stocked chemical product
Molecular Weight
-
Approximately 757.9 g/mol (theoretical value; variation possible due to counterions or residual solvents)
Structure
-
Glutamic acid core with stearic acid at α-carboxyl
-
γ-carboxyl modified with amide-linked AEEA-AEEA spacer ending in OSu ester
Biological Activity
-
Inherent activity unlikely; depends on conjugated molecules
-
Stearic acid promotes membrane affinity
-
AEEA linkers provide biocompatibility, reduce nonspecific binding
-
Glutamic acid scaffold may affect biological recognition or metabolism
Purity and Microbial Contamination
| Purity and Microbial Contamination | Specification |
|---|---|
| Purity | >90%, ideally >95% by HPLC |
| Microbial contamination | Important for in vivo use; should be minimal |
| Endotoxin levels | Should be controlled |
| Certificate of Analysis (CoA) | Includes purity, residual solvent, endotoxin data |
Identity and Quality Control
| Identity and Quality Control | Specification |
|---|---|
| Mass Spectrometry (MS) | Confirms molecular weight |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (¹H & ¹³C NMR) | Confirms chemical structure |
| High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) | Evaluates purity and impurity profile |
| Functionality assays | Verifies OSu ester reactivity (e.g., model amine reaction) |
| Free carboxylic acid presence | Confirmed by analytical methods |
Shelf Life and Storage
-
Store at −20°C in dry, inert atmosphere (argon or nitrogen)
-
Protect from light and moisture
-
OSu ester is hydrolytically sensitive; avoid water exposure
-
Shelf life typically 6–12 months
Application
-
Membrane-targeting drug delivery by conjugating drugs to lipophilic anchors
-
Lipopeptide synthesis with enhanced membrane affinity
-
Protein surface modification for membrane interaction, targeting amine groups
-
Nanoparticle functionalization with amphiphilic features for targeting and biocompatibility
-
Biomaterial design incorporating hydrophobic and hydrophilic elements
Key Characteristics
-
Heterobifunctional: stearic acid (lipophilic) and OSu ester (amine-reactive)
-
Amphiphilic molecule combining hydrophobic and hydrophilic elements
-
Biocompatible AEEA linker units reduce steric hindrance and nonspecific interactions
-
OSu ester reacts specifically with primary amines to form stable amide bonds
-
Glutamic acid scaffold enables branching and conjugation versatility
-
Extended hydrophilic spacer improves molecular flexibility and conjugation efficiency
Citation
-
Lipopeptide Synthesis: search “Synthesis and biological activity of lipopeptides”
-
Stearic Acid Conjugation: “Stearic acid-modified nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery”
-
OSu Ester Chemistry: “NHS ester-mediated protein conjugation”
-
AEEA Linkers: “AEEA linkers improve peptide solubility and reduce aggregation” (Bioconjugate Chemistry)
-
Membrane-Anchoring Peptides: “Design and synthesis of membrane-anchoring peptides”
-
Glutamic Acid Scaffolds: “Glutamic acid-based dendrimers for drug delivery”
-
Amphiphilic Molecules: “Amphiphilic polymers for drug encapsulation and delivery”
-
NHS Ester Protein Modification: “One-step protein modification using activated esters” (Bioconjugate Chemistry)
-
PEG-based NHS Crosslinkers: “Homobifunctional and heterobifunctional PEG crosslinkers” (Biomaterials)
-
Lipid-Modified Bioconjugates: “Lipid modification enhances cellular uptake of bioconjugates” (Journal of Controlled Release)
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.