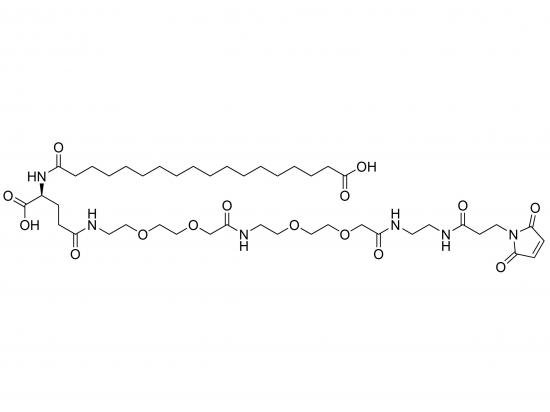
HO-Ste-Glu(AEEA-AEEA-Mal)-OH is a synthetic heterobifunctional crosslinker centered on a glutamic acid scaffold. It features a stearic acid (Ste) moiety with a free hydroxyl group at the α-carboxyl position, linked via ester or amide bond, and a maleimide (Mal) group attached to the γ-carboxyl via a flexible, hydrophilic spacer of two AEEA units. The stearic acid provides a lipophilic anchor for membrane insertion or hydrophobic interactions, while the AEEA linkers enhance solubility and biocompatibility by reducing steric hindrance and nonspecific interactions. The maleimide selectively reacts with thiols to form stable thioether bonds, enabling efficient bioconjugation. The glutamic acid framework offers two carboxyl groups for further modification, making this linker highly useful for membrane-targeting drug delivery systems, protein surface modification, nanoparticle functionalization, and related biomaterials.
Appearance
-
White to off-white solid or viscous liquid
-
Amphiphilic, potentially forming micelles in aqueous solution
Source
-
Chemically synthesized by specialized bioconjugation reagent manufacturers or custom synthesis laboratories
-
Typically not stocked by general chemical suppliers
Molecular Weight
-
Approximately 741.9 g/mol (theoretical value; can vary slightly depending on counterions, protecting groups, or residual solvents)
Structure
-
Glutamic acid central scaffold
-
Stearic acid at α-carboxyl linked via ester/amide with free hydroxyl (HO-Ste)
-
γ-carboxyl modified with amide-linked AEEA-AEEA chain terminating in maleimide
Biological Activity
-
No inherent biological activity; activity depends on conjugated molecules
-
Stearic acid enables membrane affinity and hydrophobic interactions
-
AEEA linkers improve biocompatibility and lower nonspecific binding
-
Glutamic acid scaffold may influence cellular interactions
Purity and Microbial Contamination
| Purity and Microbial Contamination | Specification |
|---|---|
| Purity | >90%, ideally >95% by HPLC |
| Microbial contamination | Concern if used for in vivo applications |
| Endotoxin levels | Should be minimized |
| Certificate of Analysis (CoA) | Specifies purity, residual solvents, endotoxin |
Identity and Quality Control
| Identity and Quality Control | Specification |
|---|---|
| Mass Spectrometry (MS) | Confirms molecular weight |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (¹H & ¹³C NMR) | Confirms chemical structure |
| High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) | Assesses purity and impurity profile |
| Functional tests | Validates maleimide reactivity (e.g., with model thiol) |
| Verification of free carboxylic acids | Confirmed by analytical methods |
Shelf Life and Storage
-
Store at –20°C, in a dry, inert atmosphere (argon or nitrogen)
-
Protect from light and moisture
-
Maleimide is sensitive to hydrolysis; avoid exposure to water
-
Shelf life typically 6–12 months
Applications
-
Membrane-targeting drug delivery: conjugation of drugs to lipophilic anchors
-
Lipopeptide synthesis: creating peptides with membrane affinity
-
Protein modification: attaching proteins for membrane interaction studies
-
Nanoparticle functionalization: combining lipophilic and hydrophilic components for targeting and biocompatibility
-
Biomaterials: incorporating amphiphilic features for advanced material design
Key Characteristics
-
Heterobifunctional: lipophilic stearic acid and thiol-reactive maleimide
-
Amphiphilic nature combining hydrophobic and hydrophilic (AEEA) elements
-
Biocompatible due to PEG-like AEEA linkers
-
Selective thiol reactivity of maleimide
-
Glutamic acid scaffold enables branching and further conjugation
-
Extended, flexible hydrophilic spacer improves solubility and reduces steric hindrance
Citation
-
Lipopeptide Synthesis: Search “Synthesis and biological activity of lipopeptides”
-
Stearic Acid for Membrane Targeting: Search “Stearic acid-modified nanoparticles for cancer drug delivery”
-
Maleimide Chemistry: Search “Maleimide-thiol coupling for protein conjugation”
-
AEEA Linkers: Search “AEEA linkers improve peptide solubility and reduce aggregation”
-
Membrane-Anchoring Peptides: Search “Design and synthesis of membrane-anchoring peptides”
-
Glutamic Acid Scaffolds: Search “Glutamic acid-based dendrimers for drug delivery”
-
Amphiphilic Molecules: Search “Amphiphilic polymers for drug encapsulation and delivery”
-
Lipid-Modified Proteins: Search “Post-translational lipidation of proteins”
-
Cell Penetrating Peptides: Search “Lipid modification enhances peptide cell penetration”
-
Thiol-Reactive Linkers: Search “Thiol-reactive linkers for site-specific protein conjugation”
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.