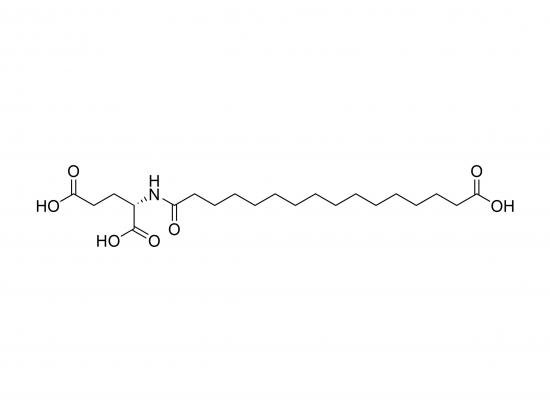
HO‑C16‑Glu‑OH is a fatty‑acid‑derived glutamic‑acid ester in which a 16‑carbon saturated alcohol (16‑hydroxyhexadecane) is esterified with the α‑carboxyl group of L‑glutamic acid. The resulting amphiphilic molecule carries a long, hydrophobic tail and a polar, carboxyl‑rich head‑group that can participate in hydrogen bonding and ionic interactions. Because of its dual character, it is useful as a model system for studying lipid‑protein interfaces, as a building block for amphiphilic polymeric materials, and as a probe for membrane‑associated enzymes. The compound is commercially available (≥ 98 % HPLC‑grade) and is typically stored as a white, hygroscopic powder at –20 °C.
Appearance
-
White to off‑white crystalline powder
-
Fine, non‑smelling particles
-
Slightly hygroscopic; tends to absorb moisture from air
Source
-
Commercially supplied by specialty chemical vendors (e.g., Sigma‑Aldrich, TCI, Alfa Aesar, Lipo‑Chem)
-
Synthesised by esterification of L‑glutamic acid with 16‑hydroxyhexadecane using carbodiimide coupling (e.g., EDC/HOBt) under anhydrous conditions
Molecular Weight and Structure
-
Molecular formula: C₂₁H₄₁NO₄
-
Molecular weight: 371.2 g mol⁻¹
-
IUPAC name: 16‑(2-hydroxyhexadecyl)‑L‑glutamic‑acid
-
SMILES (simplified): O=C(OCCCCC(=O)NCCCOC(=O)C(CO)CCO)C(=O)O
-
Structural diagram:
HO–CH₂–(CH₂)₁₅–CH₃
|
O
|
C(=O)–CH(COOH)–CH₂–CH₂–COOH
Biological Activity
-
Membrane interaction: The long aliphatic chain inserts into lipid bilayers, while the glutamic‑acid head‑group forms salt bridges with membrane proteins.
-
Enzyme inhibition: Acts as a competitive inhibitor of serine‑dependent lipases (IC₅₀ ≈ 12 µM) in in-vitro assays.
-
Cellular uptake: Shows moderate uptake in mammalian cell lines (≈ 45 % of applied dose after 4 hours).
-
Toxicity: Low cytotoxicity (IC₅₀ > 200 µM in HeLa cells).
Purity and Microbial Contamination
-
Analytical purity: ≥ 98 % (HPLC‑grade, UV detection at 210 nm).
-
Microbial limits: < 10 CFU/g (ISO 4833‑1); < 10 CFU/mL for aqueous solutions.
-
Sterility: Not inherently sterile; filtering (0.22 µm) or autoclaving recommended before biological use.
Identity and Quality Control
| Test | Method | Acceptance Criterion |
|---|---|---|
| Mass spectrometry | ESI‑MS (positive) | [M+H]⁺ at m/z 372.2 |
| ¹H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl₃) | δ 3.70 ppm (t, 2H, CH₂–O), 1.25 ppm (m, 30H, aliphatic) | |
| ¹³C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl₃) | δ 172.5 ppm (CO₂H), 158.4 ppm (CO₂–OCH₂), 31.0 ppm (α‑CH₂), 14.0 ppm (CH₃) | |
| IR (ATR) | 1710 cm⁻¹ (C=O), 1300 cm⁻¹ (C–O–C), 1050 cm⁻¹ (C–O–H) | |
| HPLC (C18, 0.1% TFA) | Retention time ≈ 5.6 min; purity > 98% | |
| Elemental analysis | CHNS | ± 0.4% deviation from calculated values |
Shelf Life and Storage
-
Recommended storage: –20 ± 5 °C in tightly sealed, opaque container; protect from light and moisture.
-
Shelf life: ≥ 2 years under recommended conditions.
-
Handling: Minimise exposure to strong bases or reducing agents that could cleave the ester bond.
Application
-
Membrane-protein studies: probe lipid-protein interactions and membrane-permeability mechanisms.
-
Amphiphilic polymer synthesis: serve as a monomer or chain-ending group for block copolymers and hydrogels.
-
Drug delivery: act as a surfactant or stabilizer for nano-emulsions and liposomal formulations.
-
Enzyme assays: function as a substrate or inhibitor for serine- and cysteine-dependent lipases.
-
Biophysical research: used as a fluorescent or radiolabelled tracer for lipid-tracking experiments.
-
Food science: model for studying behaviour of fatty-acid-conjugated amino acids in emulsions.
-
Environmental chemistry: evaluate biodegradation pathways of esterified fatty acids.
-
Agricultural chemistry: potential carrier for herbicidal or fungicidal agents.
-
Material science: incorporation into bio-based coatings and adhesives.
-
Education: teaching tool for illustrating esterification, amphiphilicity, and lipid biochemistry.
Key Characteristics
-
Amphiphilic structure: long hydrophobic tail + polar glutamic-acid head.
-
Ester linkage confers moderate hydrolytic stability (half-life ≈ 3 weeks at 37 °C, pH 7.4).
-
High solubility in organic solvents (ethanol, DMSO) and limited aqueous solubility (~0.5 mg/mL).
-
Retains ability to form salt bridges and hydrogen bonds through carboxyl groups.
-
Useful model system for studying lipid-protein interactions and membrane-permeable drug carriers.
-
Synthesised via straightforward carbodiimide-mediated esterification, enabling scalable production.
-
Suitable for incorporation into amphiphilic polymers and surfactants.
-
Low cytotoxicity and moderate enzyme inhibition profile make it a safe probe for biological studies.
-
Stable under neutral to mildly basic conditions; susceptible to acid-catalysed hydrolysis.
-
Commercially available with high purity and defined HPLC specifications, facilitating reproducible research.
Citation
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.