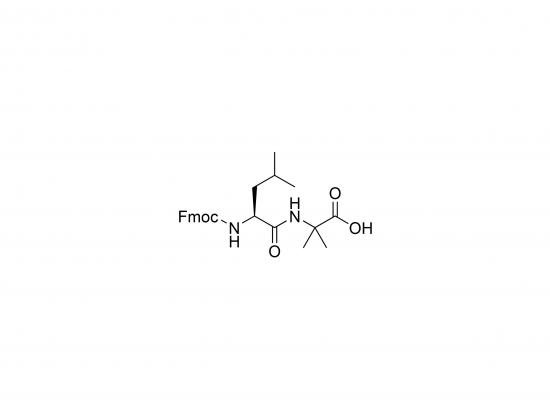
Fmoc-Leu-Aib-OH is a dipeptide building block frequently utilized in solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) for constructing peptides with tailored structural properties. It combines leucine (Leu), a hydrophobic amino acid commonly found in proteins, with α-aminoisobutyric acid (Aib), a non-proteinogenic amino acid known for inducing helical conformations, particularly α-helices and 310-helices. The Fmoc (9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl) group provides N-terminal protection, allowing controlled deprotection and coupling in SPPS. Aib introduces conformational constraint promoting well-defined secondary structures. Leucine adds hydrophobicity, influencing peptide-protein interactions or membrane affinity. Fmoc-Leu-Aib-OH is valuable for synthesizing peptides with enhanced stability, specific binding affinities, and desired structural characteristics relevant in drug design, biomaterials, and peptide folding studies.
Appearance
- White to off-white solid powder.
Source
- Synthetically produced through chemical synthesis. Commercially available from peptide synthesis reagent suppliers.
Molecular Weight and Structure
-
Molecular Weight: Approximately 438.5 g/mol (based on formula C24H28N2O5)
-
Structure consists of:
-
Fmoc (9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl) protecting group at N-terminus
-
Leucine (Leu) residue
-
α-Aminoisobutyric acid (Aib) residue
-
Free carboxyl group at C-terminus
-
-
For chemical structure, please refer to chemical databases such as PubChem or ChemSpider.
Biological Activity
-
Generally biologically inactive as isolated dipeptide.
-
Biological activity depends on the larger peptide sequence it’s incorporated into.
-
Aib strongly influences peptide conformation; Leu contributes hydrophobic interactions relevant for peptide-protein binding or membrane affinity.
Purity and Microbial Contamination
-
Purity: Typically ≥ 95% by HPLC analysis.
-
Microbial contamination should be minimal or absent for biological applications.
-
Suppliers typically provide COAs with results from bacterial endotoxin tests (LAL assay) and sterility testing.
Identity and Quality Control
-
Identity confirmed by:
-
Mass Spectrometry (MS) for molecular weight verification
-
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (¹H and ¹³C NMR) spectroscopy for structural verification
-
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy for functional group confirmation
-
-
Quality confirmed by:
-
HPLC for purity
-
Optical rotation for enantiomeric purity (Leu residue)
-
Amino acid analysis after hydrolysis confirming correct composition
-
Shelf Life and Storage
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Shelf Life | Typically 1-2 years from manufacture date, consult supplier COA |
| Storage | Store at -20°C or below, under inert atmosphere (argon or nitrogen), in tightly sealed container. Protect from moisture and light. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
Application
-
Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS) building block
-
Synthesis of α-helical and 310-helical peptides
-
Peptidomimetic synthesis mimicking peptide structure and function
-
Drug discovery targeting protein-protein interactions or membrane-related conformations
-
Biomaterial design with specific structural properties
-
Studies on peptide folding and structure-function relationships
Key Characteristics
-
Fmoc protection enables base-labile N-terminal deprotection during SPPS
-
Aib promotes helical conformations and stability
-
Leucine provides hydrophobic character
-
Versatile for coupling to other amino acids to create diverse peptide sequences
-
Soluble in organic solvents such as DMF, DMSO, and acetonitrile
Citation
-
Search for “Fmoc-Leu-Aib-OH peptide synthesis” for relevant papers
-
Research on “Aib peptide helix” or “α-aminoisobutyric acid peptide conformation”
-
Articles on “helical peptide design” or “310-helical peptide synthesis” mentioning leucine
-
Studies on “leucine-rich repeat peptides” for structural contexts
-
Supplier technical datasheets and application notes
-
Databases: Reaxys, SciFinder, PubMed for chemical and biological literature
-
Search “solid phase peptide synthesis” + “Aib” + “Leu” to find related work
-
Papers on Aib-containing peptides with enhanced stability and membrane interaction
-
Google Scholar searches with keywords like “Fmoc-Leu-Aib-OH synthesis,” “Aib Leu peptide helix,” or “Aib conformation”
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.