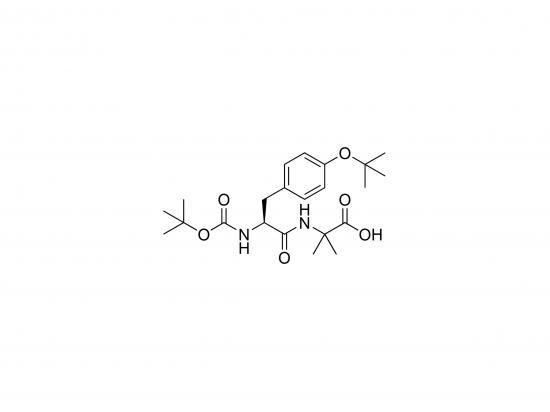
Boc-Tyr(tBu)-Aib-OH is a dipeptide building block used in peptide synthesis, comprising L-tyrosine protected at the amino group with a tert-butyloxycarbonyl (Boc) group and at the hydroxyl with a tert-butyl (tBu) group, coupled to α-aminoisobutyric acid (Aib). Aib is a non-proteinogenic amino acid known to promote α-helix formation. The acid-labile Boc and tBu protecting groups allow selective deprotection during synthesis. This dipeptide introduces a preformed Tyr-Aib motif that can enhance peptide stability, secondary structure, or receptor binding. Its bulky tBu group on tyrosine adds steric effects that may influence peptide interactions. It is widely used in research on peptide conformation and in developing peptide therapeutics.
Appearance
-
White to off-white solid or powder
Source
-
Synthesized chemically, typically by coupling Boc-Tyr(tBu)-OH to Aib-OH or derivatives
Molecular Weight and Structure
-
Molecular Weight: Approximately 448.55 g/mol
-
Structure:
-
Boc (tert-butyloxycarbonyl) protects the N-terminal amino group
-
L-Tyrosine with tBu protection on hydroxyl group
-
α-Aminoisobutyric acid (Aib) with free C-terminal carboxyl group
-
Biological Activity
-
Generally none inherent to the building block
-
Activity depends on peptide incorporation
-
Aib promotes α-helix formation, potentially affecting target interactions
-
Tyrosine is common in bioactive peptides, allowing controlled introduction
Purity and Microbial Contamination
| Test | Specification |
|---|---|
| Purity (HPLC) | Typically >95% |
| Microbial Contamination | Not a major concern for chemical grade; checked for pharmaceutical use |
Identity and Quality Control
| Test | Specification |
|---|---|
| NMR Spectroscopy | Confirms structure and purity; Boc, tBu, Tyr, Aib signals present |
| HPLC | Determines purity and impurity profile |
| Mass Spectrometry | Confirms molecular weight |
| Optical Rotation | Confirms L-tyrosine stereochemistry |
Shelf Life and Storage
| Condition | Shelf Life |
|---|---|
| Store at -20°C, protected from light and moisture | Typically 1-2 years |
Application
-
Peptide synthesis for introducing Tyr-Aib motif
-
α-helix induction via Aib incorporation
-
Synthesis of peptidomimetics
-
Research into peptide structure-function relationships
Key Characteristics
-
Protected dipeptide of L-Tyrosine and Aib
-
Acid-labile Boc and tBu protections
-
Aib promotes α-helical structure formation
Citation
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.