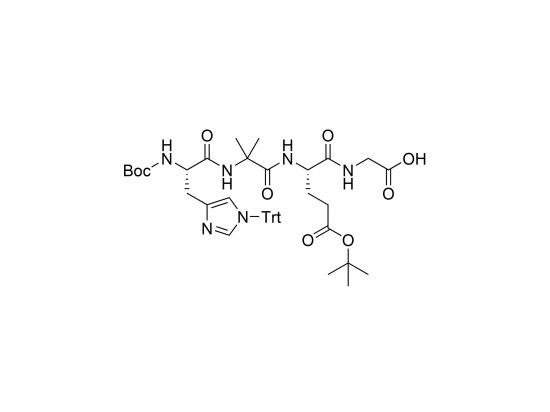
Boc-His(Trt)-Aib-Glu(OtBu)-Gly-OH is a protected tetrapeptide building block used in solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) for incorporating specific structural and functional elements into peptide chains. It consists of four amino acids: Histidine (His) with a Trityl (Trt) protecting group on the imidazole side chain, α-Aminoisobutyric acid (Aib), Glutamic acid (Glu) with a tert-butyl ester (OtBu) protecting group on the side chain carboxyl, and Glycine (Gly). The N-terminus is protected with a tert-butyloxycarbonyl (Boc) group. This protected peptide is valuable for introducing a histidine residue (for metal binding or pH-dependent interactions), Aib (to promote helical structures), and glutamic acid (for negative charge or further modification after deprotection). The Boc protecting group is acid-labile, commonly used in orthogonal protection schemes alongside Fmoc chemistry. This building block is used in synthesizing peptides with tailored properties for applications in drug discovery, biomaterials, and fundamental studies of peptide structure and function.
Appearance
-
Clear, colorless solution for subcutaneous injection.
Source
-
Produced by recombinant DNA technology in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast).
-
The insulin analogue is then synthetically modified with myristic acid.
-
Purified and formulated for pharmaceutical use.
Molecular Weight and Structure
-
Molecular weight is higher than unmodified human insulin (~5.8 kDa) due to myristic acid (C14:0) modification; approximately 5917 g/mol.
-
Structure: Human insulin sequence with threonine at position B30 removed (desB30).
-
Lysine at B29 is acylated with myristic acid via a glutamyl spacer.
Biological Activity
-
Lowers blood glucose by stimulating cellular glucose uptake and inhibiting hepatic glucose production.
-
Binds insulin receptor on muscle, liver, and fat cells to activate signaling.
-
Lysine modification promotes self-association and albumin binding, leading to prolonged half-life enabling once- or twice-daily dosing.
Application
-
Treatment of diabetes mellitus for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Key Characteristics
-
Human insulin analogue with desB30 base sequence.
-
Long-acting profile enabling once or twice daily injections.
-
Acylation at lysine B29 with myristic acid to enhance albumin binding and prolong action.
-
Activates insulin receptor-mediated pathways akin to endogenous insulin.
-
Formulated as a sterile injectable solution for subcutaneous administration.
Purity and Microbial Contamination
| Attribute | Specification |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥ 95% by HPLC analysis; required for pharmaceutical use |
| Sterility | Must meet regulatory sterility criteria; bioburden control maintained |
| Endotoxin | LAL assay ensures endotoxin levels within acceptable limits |
Identity and Quality Control
| Attribute | Specification |
|---|---|
| Mass Spectrometry (MS) | Confirms molecular weight and myristic acid modification |
| Amino Acid Analysis | Confirms correct amino acid composition of desB30 insulin analogue |
| Peptide Mapping | Verifies correct sequence and modification site |
| High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) | Evaluates purity and detects aggregates |
| Bioactivity Assays | Measures insulin receptor binding and glucose-lowering activity in vitro/in vivo |
| Immunochemical Assays | Assesses binding affinity to insulin receptor |
Shelf Life and Storage
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Shelf Life | Typically 2–3 years if stored properly; consult manufacturer’s instructions |
| Storage | Store refrigerated at 2–8°C, protect from light, do not freeze; follow post-opening instructions |
Citation
-
Overview of solid-phase peptide synthesis methods including Boc chemistry:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28238639/ -
Use of Trityl protecting group for histidine in peptide synthesis:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.joc.8b00528 -
α-Aminoisobutyric acid (Aib) influence on peptide helical structure:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022283618300638 -
Tert-butyl ester (OtBu) protecting group application in peptide synthesis:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2014.11.058 -
Strategies for orthogonal peptide protecting groups including Boc and Fmoc:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6526649/ -
Applications of histidine-containing peptides for metal ion binding:
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2019/ra/c9ra04552h -
Review of peptidomimetic synthesis techniques:
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202001378 -
Synthesis and properties of peptides incorporating Aib residues:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32890023/ -
Protecting group strategies in peptide assembly:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19382616/ -
Chemical databases with structures and synthetic pathways of protected peptides:
https://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.4440190.html
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.