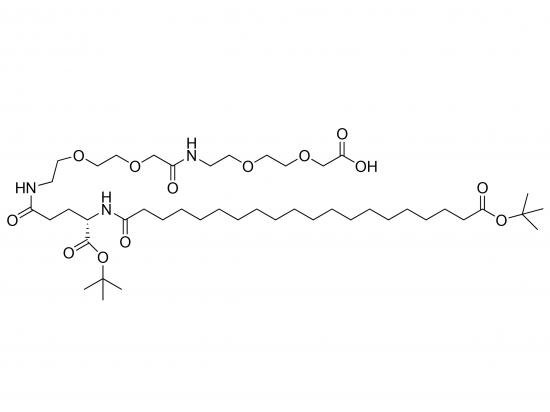
tBuO-Ara-Glu(AEEA-AEEA-OH)-OtBu is a synthetic glutamic acid derivative designed to functionalize biomolecules, surfaces, or advanced materials. It features a glutamic acid core with one carboxyl protected as a tert-butyl ester (OtBu), and the other functionalized with two sequential AEEA (2-[2-(2-aminoethoxy)ethoxy]acetic acid) units, terminating in a free carboxyl group (OH). The alpha-amino group of glutamic acid is linked to a tert-butyl-protected arabinogalactan derivative (Ara), introducing a carbohydrate moiety as a biological recognition element. The design combines a carbohydrate handle (Ara), a hydrophilic PEG-like spacer (AEEA), and an acid-labile protected carboxyl group for further conjugation, making it suitable for glycoconjugate synthesis, drug delivery, and surface modification.
Appearance
-
White to off-white solid
Source
-
Synthetically produced via chemical synthesis
-
Supplied by specialized vendors in glycan chemistry, PEGylation, and bioconjugation reagents
Molecular Weight
-
Calculated in the range of 900–1300 g/mol; exact value depends on arabinogalactan fragment size
Structure
-
Arabinogalactan derivative (tBuO-protected) linked to glutamic acid alpha-amino via amide bond
-
Glutamic acid core
-
One carboxyl protected as tert-butyl ester (OtBu)
-
Two sequential AEEA units on side chain, terminating in a free carboxyl group (OH)
Biological Activity
-
Biologically inert alone
-
Carbohydrate moiety may interact with lectins or carbohydrate-binding proteins
-
AEEA increases solubility and biocompatibility
-
Terminal carboxyl is available for conjugation
Purity and Microbial Contamination
| Purity and Microbial Contamination | Specification |
|---|---|
| Purity | Typically ≥85–90%, HPLC required |
| Microbial contamination | Minimal; COA should confirm levels |
| Testing | Endotoxin (LAL assay), sterility |
| Certificate of Analysis (CoA) | Details purity, solvent, endotoxin |
Identity and Quality Control
| Identity and Quality Control | Specification |
|---|---|
| Mass Spectrometry (MS) | Confirms molecular weight |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (¹H & ¹³C NMR) | Verifies chemical structure |
| Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy | Identifies functional groups |
| High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) | Purity assessment |
| Carbohydrate analysis | Confirms arabinogalactan identity |
| Acid value determination | Quantifies free carboxyl group |
Shelf Life and Storage
-
Shelf life: 6–12 months (shorter than simple reagents; refer to supplier COA)
-
Store at –20°C or below in airtight, dry, inert container (argon or nitrogen atmosphere)
-
Protect from moisture and light
Applications
-
Glycoconjugate synthesis: targeted conjugation for biological recognition
-
Drug delivery: crafting systems with carbohydrate-lectin targeting
-
Surface modification: adding carbohydrate coatings for cell/material interaction
-
Biomaterials: building new materials with precise biological targeting properties
Key Characteristics
-
Carbohydrate moiety (Arabinogalactan–Ara): enables biorecognition
-
Hydrophilic AEEA spacers: provide PEG-like solubility and reduce steric hindrance
-
Reactive carboxyl group: available for activation and further conjugation
-
tBu protection: acid-labile protection for controlled deprotection
Citation
-
Search “arabinogalactan protein conjugate” and “carbohydrate protein conjugation”
-
Explore “PEGylation protein conjugation,” “AEEA linker modification,” “carboxyl activation carbohydrate”
-
Review supplier technical notes for glycan reagents and bioconjugation supplies
-
Consult Reaxys/SciFinder for related chemical structures
-
Investigate “glycoconjugate synthesis,” “glycopeptide synthesis,” “glycoconjugate drug delivery”
-
Use Google Scholar keywords: “arabinogalactan protein conjugate,” “AEEA protein conjugation,” “carboxyl activation carbohydrate,” and “glycoconjugate drug delivery”
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.