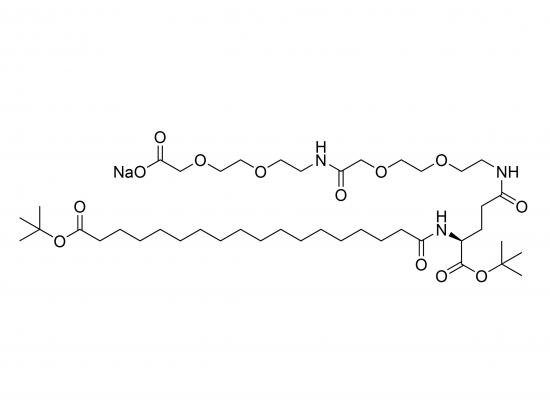
tBuO-Ste-Glu(AEEA-AEEA-ONa)-OtBu is a synthetic glutamic acid derivative designed to impart both lipophilic and hydrophilic properties to biomolecules. The molecule has a glutamic acid core with one carboxyl group protected as a tert-butyl ester (OtBu) and the other functionalized on the side chain with two sequential AEEA units. The terminal carboxyl of the second AEEA is present as a sodium salt (ONa), providing a negative charge and enhanced water solubility. The alpha-amino group of glutamic acid is linked to a stearic acid moiety with a tert-butyl ester protection, serving as a lipid anchor. This compound is useful in forming self-assembling structures, modifying membrane interactions, or creating drug delivery systems with balanced amphiphilic character.
Appearance
-
White to off-white solid, potentially waxy due to stearic acid chain
Source
-
Chemically synthesized, not naturally occurring
-
Offered by specialized chemical suppliers focused on PEGylation, lipid modification, and bioconjugation reagents
Molecular Weight
-
Estimated between 800–1100 g/mol, depending on exact chemical variants
Structure
-
Stearic acid (tBuO-protected) attached via amide bond to glutamic acid α-amino group
-
Glutamic acid core with one carboxyl protected as OtBu
-
Two AEEA units linked via amide bonds sequentially on side chain carboxyl
-
Terminal carboxyl of second AEEA ionized as sodium salt (ONa)
Biological Activity
-
Typically biologically inert alone
-
Stearic acid provides membrane affinity
-
AEEA linkers increase hydrophilicity and reduce steric hindrance
-
Sodium carboxylate adds negative charge, enhancing solubility
-
Bioactivity depends on conjugated partners
Purity and Microbial Contamination
| Purity and Microbial Contamination | Specification |
|---|---|
| Purity | Typically ≥90%, validated by HPLC |
| Microbial contamination | Minimal levels expected |
| Testing | LAL assay for endotoxin, sterility tests |
| Certificate of Analysis (CoA) | Includes purity, solvent residues, endotoxin |
Identity and Quality Control
| Identity and Quality Control | Specification |
|---|---|
| Mass Spectrometry (MS) | Confirms molecular weight |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) (¹H, ¹³C) | Validates structure and purity |
| Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy | Confirms functional groups |
| High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) | Purity assessment |
| Sodium content analysis | Confirms ionization status |
Shelf Life and Storage
-
Expected shelf life 6–12 months, possibly shorter due to compound complexity
-
Store at –20°C or below, tightly sealed under inert atmosphere (argon or nitrogen)
-
Protect from moisture and light
Applications
-
Lipid anchoring: attaching molecules to membranes or lipid bilayers
-
PEGylation: imparting hydrophilicity and flexibility to biomolecules
-
Drug delivery: enhancing water solubility, membrane permeability, and targeting
-
Self-assembling systems: incorporation into micelles, liposomes, or nanostructures
-
Surface modification: generating hydrophobic/hydrophilic coatings
Key Characteristics
-
Lipophilic stearic acid chain for membrane interaction
-
Hydrophilic PEG-like AEEA linker units improve solubility and reduce steric hindrance
-
Negative charge from sodium carboxylate improves aqueous compatibility
-
tBu protection allows controlled chemical synthesis steps
Citation
-
Search terms like “stearic acid protein modification,” “lipid conjugation protein,” “AEEA protein linker,” and “PEGylation drug delivery”
-
Review lipopeptide synthesis and lipid-modified conjugate literature
-
Consult technical data sheets from bioconjugation reagent suppliers
-
Use chemical databases (Reaxys, SciFinder) to find related compounds and papers
-
Search “liposome PEGylation” and “self-assembling lipid-polymers” for applications
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.