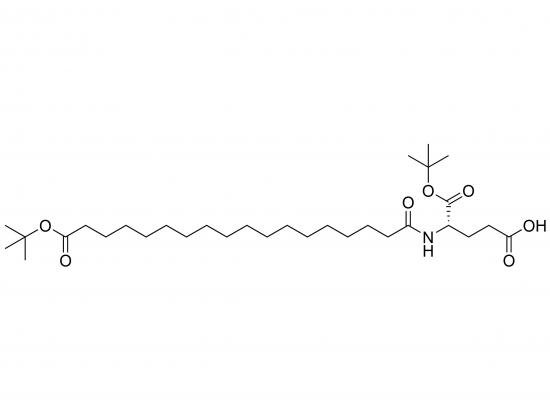
tBuO-Ste-Glu(OtBu)-OH is a lipidated, protected glutamic acid building block frequently used in solid-phase peptide synthesis for research and development. It comprises a glutamic acid residue with both carboxylic acids protected as tert-butyl (tBu) esters, and a lipophilic stearoyl (Ste) group attached to the N-terminus via an amide bond. The tBu groups are acid-labile, permitting selective deprotection. This molecule is a key tool for synthesizing lipidated peptides with enhanced membrane permeability or solubility.
Appearance
-
White to off-white solid or powder
Source
-
Produced synthetically via chemical synthesis
Molecular Weight and Structure
-
Molecular Weight: ~570–600 g/mol (depends on exact stereochemistry)
-
Structure:
-
Stearoyl (C18 saturated fatty acid) at N-terminus
-
Glutamic acid (Glu) core
-
Both carboxyl groups protected with tert-butyl (OtBu) esters
-
Biological Activity
-
No direct inherent biological activity
-
Biological effect derives from incorporation into peptides or conjugates
-
Stearoyl group enhances lipophilicity and membrane interaction properties
Purity and Microbial Contamination
-
Purity: >95% (HPLC)
-
Microbial contamination: <100 CFU/g
Identity and Quality Control
-
NMR spectroscopy: Confirms structure and purity
-
HPLC: Determines purity and impurities
-
Mass spectrometry: Confirms molecular weight
-
Optical rotation: Confirms stereochemistry (if applicable)
Shelf Life and Storage
-
Shelf life: 1–2 years (properly stored)
-
Storage: –20°C, protected from light and moisture
Application
-
Building block in SPPS for lipidated peptide synthesis
-
Used to increase solubility, stability, or membrane permeability of peptides
-
Research on the impact of lipidation on peptide pharmacokinetics and activity
Key Characteristics
-
Lipidated, protected glutamic acid (Stearoyl + OtBu groups)
-
Acid-labile tBu protecting groups
-
Enhances membrane permeability and solubility
Citation
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.